
cognitive science lab.
Our mission is to do scientific investigation on implicit and explicit processes in human perception, cognition, and action. Recent projects include investigations of implicit and explicit processes of sequence learning and how action-effect influences emergence or modulation of sense of agency.
News
- 入学関係
- Apr/2024
吉良瑞希さん(修士課程学生), 李翔宇さん(修士課程学生), 蔡心儀さん(研究生),および吉村可奈子さん(技術補佐員)が本研究室に加入しました.
- Dec/2023
感覚間協応の分類に関する論文が,国際誌 PLOS ONEに掲載されました.
Ohtake, Y., Tanaka, K., & Yamamoto, K. How many categories are there in crossmodal correspondences? A study based on exploratory factor analysis. - Dec/2023
日本基礎心理学会第42回大会(2023/12/1-3)にて1件の発表を行いました.
- Oct/2023
李翔宇さん(研究生)および小池飛雄馬さん(技術補佐員)が本研究室に加入しました.
- Apr/2023
林元浩さん(修士課程学生)および石井清花さん(技術補佐員)が本研究室に加入しました.
- Mar/2023
名古屋大学・青山ユニット主催WSにて,招待講演を行いました.
- Mar/2023
ドイツ・ケルン大学のSarah Esser博士,Hilde Haider教授,Clarissa Lustig博士との共同研究論文が国際誌Psychological Researchに掲載されました.
Esser, S., Haider, H., Lustig, C., Tanaka, T., & Tanaka, K. Action–effect knowledge transfers to similar effect stimuli. - Dec/2022
時間感覚の中心化傾向に関する論文が,国際誌i-Perceptionに掲載されました.
Ueda, N.*, Tanaka, K.*, & Watanabe, K.(*equal contribution). Memory decay enhances central bias in time perception. - Oct/2022
林元浩さんが研究生として本研究室に加入しました.
- Aug/2022
アクションと記憶に関する論文が,国際誌Frontiers in Psychologyにアクセプトされました.
Shimane, D., Tanaka, T., Watanabe, K., & Tanaka, K. Motor engagement enhances incidental memory for task-irrelevant items. - Feb/2022
第21回感性学研究会にて招待講演(「主体的な行為を支える認知システム」)を行いました.
- Feb/2022
日本心理学会第85回 学術大会特別優秀発表賞を以下の研究で受賞しました.
大竹 裕香・田中 観自・山本 健太郎,視聴覚間における感覚間協応の因子構造の探索 - Dec/2021
統合失調症患者の時間知覚に関する共同研究論文が国際誌Schizophrenia Research: Cognitionに採択されました.
Ueda, N., Tanaka, K., Maruo, K., Roach, N., Sumiyoshi, T., Watanabe, K., & Hanakawa, T. Perceptual inference, accuracy, and precision in temporal reproduction in schizophrenia. - Dec/2021
日本基礎心理学会第40回大会にて1件の発表を行いました.
- Oct/2021
スイス・フリブール大学のRoberto Caldara博士率いる研究グループとの共同研究論文が国際誌Journal of Visionにアクセプトされました.
de Lissa, P., Sokhn, N., Lasrado, S., Tanaka, K., Watanabe, K., & Caldara, R. Rapid saccadic categorization of other-race faces. - Aug/2021
日本心理学会 第85回大会(2021/9/1-8)にて以下の発表を行います.
大竹 裕香・田中 観自・山本 健太郎,視聴覚間における感覚間協応の因子構造の探索 - Apr/2021
The 32nd International Congress of Psychology (ICP 2020+;2021/7/18-23), Prague, Czech Republic.にて以下の発表を行います.
Tanaka, T. & Tanaka, K., The flash-grab effect decreases when the flash is caused by action. - Apr/2021
The 2021 Vision Sciences Society meeting (2021/5/21-26), Online conferenceにて以下の発表を行います.
Tanaka, T. & Tanaka, K., The temporal window of attention to self-generated stimuli. - Oct/2020
反応促進に関する論文が,国際誌 Experimental Brain Researchにアクセプトされました.
Tanaka, T., Watanabe, K., & Tanaka, K. Immediate action effects motivate actions based on the stimulus-response relationship. - Oct/2020
自己主体感に関する論文が,国際誌 Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performanceにアクセプトされました.
Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. Sense of agency with illusory visual events. - July/2020
日本心理学会第84回大会(2020/9/8-10)にて以下の発表を行います.
田中拓海・島根大輔・渡邊克巳・田中観自,行動の直後に知覚された刺激の記憶は増強される - July/2020
42nd Annual Virtual Meeting of the Cognitive Science Society (2020/7/29-8/1; Virtual Meeting)にて以下の発表を行います.
Tanaka, T., Watanabe, K., & Tanaka, K. Immediate action-effects facilitate response speed via stimulus-response association - May/2020
カナダ・トロント大学のTristan Loria博士とLuc Tremblay博士との共同研究の論文 が国際誌 Attention, Perception, & Psychophysicsにアクセプトされました.
Loria, T., Tanaka, K., Watanabe, K., & Tremblay, L. Deploying attention to the target location of a pointing action modulates audio-visual processes at non-target locations. - Apr/2020
田中拓海さんが学術研究員として本研究室に着任されました.
- Nov/2019
日本基礎心理学会第38回大会(2019/11/29-12/1)で3件の発表を行います.
- Oct/2019
学術研究員の公募情報が公開されました.公募は終了しました. - Sep/2019
研究室のHPを開設しました.

Research
Implicit transfer in visuomotor sequence learning
Learning behavioral sequences, such as typing on a keyboard, is vital in our daily life. Past studies have investigated how people implicitly or explicitly learn a sequence by adopting various experimental paradigms (e.g., artificial grammar learning, the discrete sequence production task, the visuomotor button press task, and the serial reaction time task). We mainly used the visuomotor button press task (hereafter called the m × n task; Hikosaka et al., 1995, J. Neurophysiol.). As you can watch in a movie on the left side, participants are required to learn a pre-determined pattern by trial-and-error. In the first learning phase (top movie), their error rate and reaction time were high and slow, but their performances became highly fluent in the late learning phase (bottom movie).
The main results of our research projects showed that people could implicitly transfer their obtained skills to a new sequence (Tanaka & Watanabe, 2014a, Cognitive Science, 2014b, Acta Psychologica). In our experiment, after participants learned a 3 × 7 sequence (i.e., learning session), the spatial configuration of the sequence was vertically mirrored (i.e., transfer session), for example. Notably, the experimenter instructed the participants to learn a newly generated sequence again (i.e., he/she did not instruct the rule of transformation). Then, after their completion, the experimenter interviewed them whether they were able to verbalize what they found in the second (transfer) session. Interestingly, those who could not report any rules performed the vertically mirrored sequence better than those who performed a randomly generated sequence (control group), indicating implicit transfer of the learned sequence.
In addition, we also have investigated the effects of learning methods in the m × n sequence (Tanaka & Watanabe, 2016, Acta Psychologica), explicit instruction of rules on skill transfer (Tanaka & Watanabe, 2017, Experimental Brain Research), and effects of model skills on observational learning (Tanaka & Watanabe, 2018, Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology). Currently, we are interested in the roles of action-effects on sequence learning (e.g., Tanaka & Watanabe, 2017, Frontiers in Psychology).
早稲田大学高等研究所在籍時(2018年度)に受けた系列学習に関する取材内容はこちらのリンクから御覧いただけます.
- Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. (2014a), Implicit transfer of reversed temporal structure in visuomotor sequence learning. Cognitive Science, 38(3), 565-579.
- Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. (2014b), Implicit transfer of spatial structure in visuomotor sequence learning, Acta Psychologica, 153, 1-12.
- Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. (2016). Impacts of visuomotor sequence learning methods on speed and accuracy: Starting over from the beginning or from the point of error. Acta Psychologica, 164, 169-180.
- Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. (2017). Explicit instruction of rules interferes with visuomotor skill transfer. Experimental Brain Research, 235(6), 1689-1700.
- Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. (2017). Effects of an additional sequence of color stimuli on visuomotor sequence learning. Frontiers in Psychology, 8:937.
- Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. (2018). Effects of model types in observational learning on implicit sequential learning. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 71(7), 1596-1606.
Retrospective modulation of Sense of agency
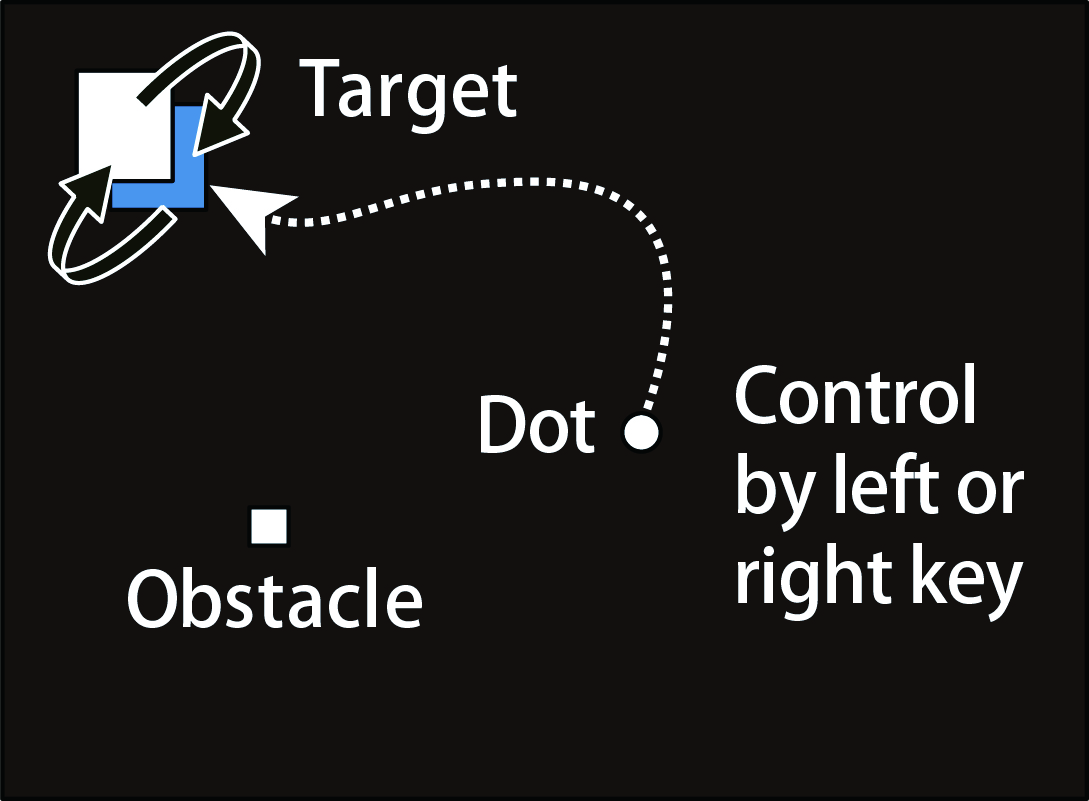
Sense of agency (SoA) is a subjective feeling of being in control of one's own actions and causing external events (Gallagher, 2000, Trends in Cognitive Science). For example, if a light around a person turned on immediately after he/she pressed a button, he/she likely felt that his/her action caused this result. We are interested in how SoA emerges, the environment modulates SoA, SoA can influence the following action or learning, and we can measure SoA (implicit and explicit measurement).
In our recent projects (Oishi, Tanaka, & Watanabe, 2018, PLoS One, 2019, Acta Psychologica), we focused on continuous actions closer to a situation in our daily lives. In one of our experiments, participants carried a white dot with a delay to a target square while avoiding obstacle squares (left panel). The color of the target changed unpredictably between white and blue. If the dot reached the target while it was white or blue, a trial was considered as successful or failed. Thus, actions (control of the white dot) during the task should result in almost identical experiences of successful and failed trials. After each trial, the participants reported to what extent they felt they had been in control of the dot. The results showed that SoA was higher with a shorter delay between button press and dot movement (i.e., easier control) and successful trials. These findings indicate that the sense of online control and the evaluation of continuous action based on feedback independently influence SoA. Remarkably, the evaluation retrospectively modulated SoA.
- Oishi, H.*, Tanaka, K.*, & Watanabe, K. (*equal contribution) (2019). Sense of agency in continuous action is influenced by outcome feedback in one-back trials, Acta Psychologica, 199, 102897.
- Oishi, H.*, Tanaka, K.*, & Watanabe, K. (*equal contribution) (2018). Feedback of action outcome retrospectively influences sense of agency in a continuous action task. PLoS ONE, 13(8): e0202690.
アクションエフェクトによる反応促進
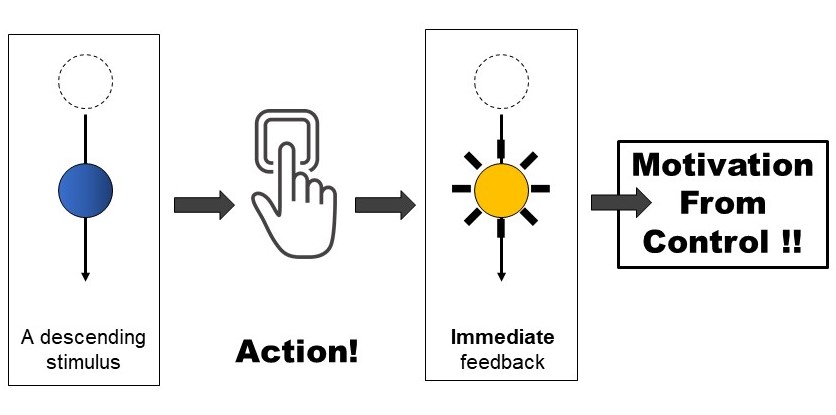
ターゲット刺激に対する行為の後に感覚フィードバック(例:刺激のフラッシュや音の呈示など)が提示されたとき,即時的な場合の方が(遅延なし)遅延を伴う場合に比べて(600msなど),反応時間が短くなることが知られています(Eitam et al., 2013, Experimental Branin Research).その発生機序は制御感から生じる動機づけである可能性など,現在も議論が続いています.我々の研究チームは先行研究の再現に成功し,また刺激ー行為ーフィードバックの連合が反応促進に寄与することも示しました(Tanaka et al., 2021, Experimental Brain Research).現在も,自己主体感などとの関わりをキーワードにその詳細なメカニズムについて検討を重ねています.
- Tanaka, T., Watanabe, K., & Tanaka, K. (2021). Immediate action effects motivate actions based on the stimulus–response relationship. Experimental Brain Research, 239(1), 67-78.
アクションと記憶
自身の行動に近接して提示された刺激は,行動をしていない時に提示された刺激に比べてよく記憶されることが知られています(e.g., Yebra et al., 2019, Nature Communication).しかし,行動に関わる一連の処理(運動の計画,実行および行動結果の知覚など)において,どの段階が記憶の増強に寄与しているのかは,現在議論が続いています.我々の研究チームは,行動と刺激提示の時間的関係に着目し,記憶の促進効果のメカニズムについて検討をしています.
- Shimane, D., Tanaka, T., Watanabe, K., & Tanaka, K. (2021). Post-action memory enhancement: Exploring the temporal relationship between action and memory formation. Psyarxiv.
- Shimane, D., Tanaka, T., Watanabe, K., & Tanaka, K. (2022).Motor engagement enhances incidental memory for task-irrelevant items. Frontiers in Psychology, 5007.
心理的時間と精神疾患
古くから精神疾患の方の訴えとして,「時間の感覚がわからなくなってしまった」「現実感がなくなった」などの主観的な知覚の変化があることが知られています.私たちの知覚は,実際に環境から入力される感覚だけでなく,それまでに経験された感覚にも影響されています (Shi, Church & Meck., 2013, Trends in Cognitive Science).我々の研究チームは,このような過去に経験した感覚と現在入力される感覚の統合のメカニズムと,主観的な知覚が変化する精神疾患症状との関連について明らかにしようとしています.
- Ueda, N., Tanaka, K., Maruo, K., Roach, N., Sumiyoshi, T., Watanabe, K., & Hanakawa, T. (2022). Perceptual inference, accuracy, and precision in temporal reproduction in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research: Cognition, 28, 100229.
- Ueda, N.*, Tanaka, K.*, & Watanabe, K. (*equal contribution)(under revison).Memory decay enhances central bias in time perception
Color-Shape association
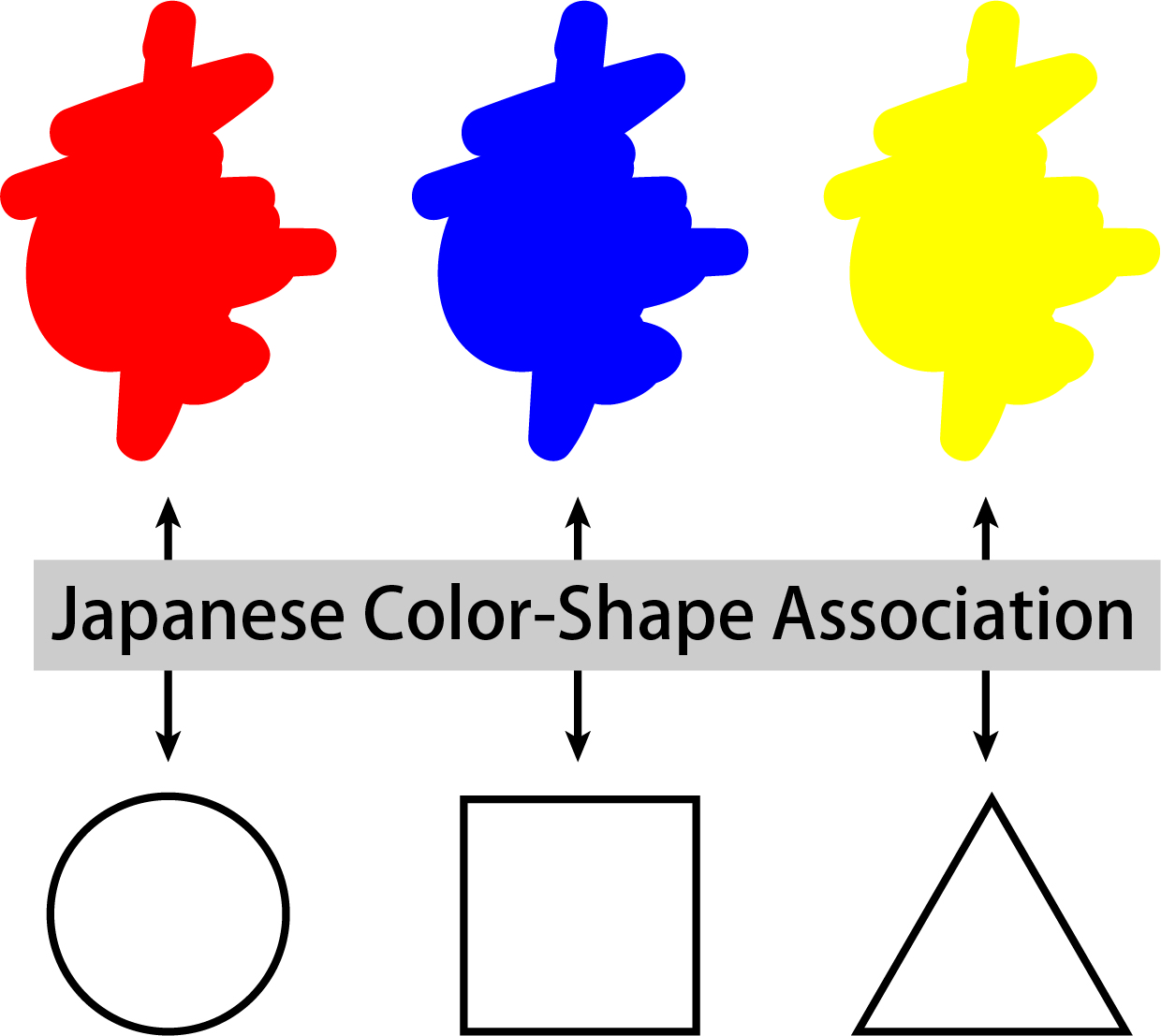
Artists and researchers have spent years examining general associations between colors and shapes. Kandinsky, a renowned abstract painter, proposed a fundamental correspondence between basic shapes and primary colors. For instance, circles, squares, and triangles are associated with blue, red, and yellow, respectively (Kandinsky, 1912, 1947).
Our research projects examined whether color-shape associations (hereafter, CSA) were unlikely influenced by differences between languages and cultures. So far, we found that Japanese participants associated shapes with specific colors, and these color–shape associations, by and large, were consistent with those in previous pieces of literature: red-circle, blue-square, and yellow-triangle. In addition, correspondence analysis indicated that most CSA could be interpreted by congruent "warmth" perception for colors and shapes. Therefore, semantic associations between visual features of color and shape might lead to the color–shape associations. The CSA was replicated even in a study using an indirect behavioral test (Implicit Association Test; Chen, Tanaka, & Watanabe, 2015, PLoS ONE). Recently, we have been interested in the developmental process of CSA.
- Chen, N., Tanaka, K., Namatame, M., & Watanabe, K. (2016). Color-Shape Associations in Deaf and Hearing People. Frontiers in Psychology, 7, 355.
- Chen, N., Tanaka, K., Matsuyoshi, D., & Watanabe, K. (2015), Associations Between Color and Shape in Japanese Observers, Psychology of Aesthetics, Creativity, and the Arts, 9(1), 101-110.
- Chen, N., Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. (2015), Color-Shape Associations Revealed with Implicit Association Tests, PLoS ONE, 10(1), e0116954-e0116954.

people
Associate Professor
Dr. Kanji Tanaka is an associate professor in the Division for Experimental Natural Science, Faculty of Arts and Science, Kyushu University. Prior to his current position, he was a JSPS research fellow DC1 and PD at the University of Tokyo, worked as a project researcher at the University of Tokyo, a JSPS research fellow PD at Waseda University and worked as an assistant professor at Waseda Institute for Advanced Study in Waseda University. He earned his PhD in 2013 from the University of Tokyo. He is interested in scientific investigations of explicit and implicit sequence learning and transfer, and recently tries to understand roles of sense of agency on learning situation.
e-mail: kanji.tanaka(at)artsci.kyushu-u.ac.jp
Google Scholar
Research map
Full CV in English (in prep)
Full CV in Japanese (in prep)
Master's Student

林 元浩 (Lin Yuanhao)
研究テーマ:ビデオゲームにおける視覚効果が運動主体感に与える影響
運動主体感は運動を通じて自身が外界の対象を制御している感覚を指し,日常生活だけではなくゲームプレイにおいても重要な役割を担っています。これまでゲームプレイによる知覚や認知の変化について検討がなされてきたものの,ゲーム特有のエフェクトが主体感の形成や変調に与える影響は未だ明らかになっていません。私はゲーム特有の視覚効果であるスクリーンシェイク効果に着目し,それがプレーヤーの運動主体感にどのような影響を与えているのかを検討しています。

吉良 瑞希 (Mizuki Kira)
研究テーマ:音楽の演奏者と聴取者における感情の差異に関する生理心理学的研究
我々は普段の生活の中で「音楽」に触れる機会は多く,音楽により誘発される感情は様々です。私は,音楽を奏でる演奏者と音楽の聴取者において生じる感情の違いに関心 があり,同じ音楽を演奏する場合と聴取する場合で,それぞれどのような感情が喚起されるのか,またその強さは異なるのかについて,主観的な評価指標や客観的な生理反応を計測することで検討したいと考えています。

李 翔宇 (Li Xiangyu)
研究テーマ:垂直方向の動作が記憶に与える影響
ボタンを押したりスクリーンをスワイプしたりするなどの動作は私たちの日常生活に欠かせません。 これまでの研究で、動作が記憶などの認知プロセスに影響を与えることが分かっており、例えば、ヒトはボタンを押した後に呈示された刺激をよく覚えることができると考えられています。 加えて、空間的メタファーに基づき、ヒトは「上」をポジティブなもの、「下」をネガティブなものと考える傾向があります。私は、上下スワイプなどの方向性のある動作が記憶にどのような影響を与えているのかについて興味があり、行動実験を通じて検討していきたいと考えています。
Research Student

蔡 心儀 (Cai Xinyi)
Technical Assistant

Sayaka Ishii

Hyuma Koike

Kanako Yoshimura

publication
and
presentation
Journal Articles
- Tanaka, T., Watanabe, K., & Tanaka, K. (2021). Immediate action effects motivate actions based on the stimulus–response relationship. Experimental Brain Research, 239, 67–78.
- Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. (2021). Sense of agency with illusory visual events. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 47(2), 238–251.
- Loria, T., Tanaka, K., Watanabe, K., & Tremblay, L. (2020). Deploying attention to the target location of a pointing action modulates audiovisual processes at nontarget locations. Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics, 82(7), 3507-3520.
- Oishi, H.*, Tanaka, K.*, & Watanabe, K. (*equal contribution) (2019). Sense of agency in continuous action is influenced by outcome feedback in one-back trials, Acta Psychologica, 199, 102897.
- Oishi, H.*, Tanaka, K.*, & Watanabe, K. (*equal contribution) (2018). Feedback of action outcome retrospectively influences sense of agency in a continuous action task. PLoS ONE, 13(8): e0202690.
- Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. (2018). Effects of model types in observational learning on implicit sequential learning. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 71(7), 1596-1606.
- Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. (2017). Effects of an additional sequence of color stimuli on visuomotor sequence learning. Frontiers in Psychology, 8:937.
- Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. (2017). Explicit instruction of rules interferes with visuomotor skill transfer. Experimental Brain Research, 235(6), 1689-1700.
- Chen, N., Tanaka, K., Namatame, M., & Watanabe, K. (2016). Color-Shape Associations in Deaf and Hearing People. Frontiers in Psychology, 7, 355.
- Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. (2016). Impacts of visuomotor sequence learning methods on speed and accuracy: Starting over from the beginning or from the point of error. Acta Psychologica, 164, 169-180.
- Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. (2015). Effects of learning duration on implicit transfer. Experimental Brain Research, 233(10), 2767-2776.
- Chen, N., Tanaka, K., Matsuyoshi, D., & Watanabe, K. (2015), Cross preferences for colors and shapes, Color Research & Application, 1-8.
- Chen, N., Tanaka, K., Matsuyoshi, D., & Watanabe, K. (2015), Associations Between Color and Shape in Japanese Observers, Psychology of Aesthetics, Creativity, and the Arts, 9(1), 101-110.
- Chen, N., Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. (2015), Color-Shape Associations Revealed with Implicit Association Tests, PLoS ONE, 10(1), e0116954-e0116954.
- Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. (2014), Implicit transfer of spatial structure in visuomotor sequence learning, Acta Psychologica, 153, 1-12.
- Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. (2014), Implicit transfer of reversed temporal structure in visuomotor sequence learning. Cognitive Science, 38(3), 565-579.
- Hosoda, C., Tanaka, K., Nariai, T., Honda, M., & Hanakawa, T. (2013) Dynamic neural network reorganization associated with second language vocabulary acquisition: a multidimensional imaging study. The Journal of Neuroscience, 33(34), 13663-13672.
- Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. (2013) Effects of learning with explicit elaboration on implicit transfer of visuomotor sequence learning. Experimental Brain Research, 228(4), 411-425.
- Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. (2013) Interference between accustomed number-space mappings and unacquainted letter-space mappings in a button press task. Human Factors: The Journal of Human Factors and Ergonomics Society, 55(6), 1088-1100.
- Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. (2012) Overestimation and underestimation in a configural response learning task. Kansei Engineering International Journal, 11(4), 171-178.
- Tanaka, K., & Yamaoka, T. (2010) Understanding characteristics of the transfer of mental models in terms of electrical devices. Psychologia, 53(4), 256–266.
- Tanaka, K., & Yamaoka, T. (2010) Extracting and understanding the relationship between components of the capacity in elderly people in terms of electrical device comprehension. Journal of Human Ergology, 39(2), 121-131.
Proceedings
- Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. (2017) Impacts of cue reliability and explicit instruction on visual attention. Proceedings of the 2017 – 9th International Conference on Knowledge and Smart Technology (KST), 270-273. ISBN: 978-1-4673-9075-0.
- Tanaka, K., Chien, S., Yamamoto, K., & Watanabe, K. (2016) Memory distortion of depth of a visual stimulus for perception and action. Proceedings of the 2016 – 8th International Conference on Knowledge and Smart Technology (KST), 281-286. ISBN: 978-1-4673-8139-0.
- Ueda, N., Tanaka, K., &Watanabe, K. (2016) Gender differences in visuomotor sequence learning. Proceedings of the 2016 – 8th International Conference on Knowledge and Smart Technology (KST), 271-274. ISBN: 978-1-4673-8139-0.
- Yamamoto, K., Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. (2015). The role of global configuration in detection of mirror and translational symmetries. Proceedings of the 2015 - 7th International Conference on Knowledge and Smart Technology (KST), 165-168. ISBN: 978-1-4799-6049-1.
- Chen, N., Tanaka, K., Namatame, M, & Watanabe, K. (2015). Consistency of color-shape associations in deaf people. Proceedings of the 2015 - 7th International Conference on Knowledge and Smart Technology (KST), 173-175. ISBN: 978-1-4799-6049-1.
- Chen, N., Tanaka, K., Nagamori, Y., Namatame, M., & Watanabe, K. (2014) Grapheme-color association in deaf people. ACA 2014 Conference Proceedings, 169-172. ISBN 978-986-86796-4-1.
- Chen, N., Tanaka, K., Matsuyoshi, D., Nagamori, Y., Namatame, M., & Watanabe, K. (2014) Color-shape association in deaf and hearing people. Proceedings of the 2014 6th International Conference on Knowledge and Smart Technology (KST), 85-88. ISBN:978-1-4799-1424-1.
- Chen, N., Tanaka, K., Matsuyoshi, D., & Watanabe, K. (2013) Cross preference for color combination and shape. Proceedings Book of the 1st Asia Color Association Conference, 98-101. ISBN 978-974-625-619-3.
- Chen, N., Tanaka, K., Matsuyoshi, D., & Watanabe, K. (2013) Associations between colors and shapes in Japanese observers. The Proceedings of International Association of Societies of Design Research, 5811-5818. ISBN: 978-4-9980776-3-3.
- Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. (2013). Implicit transfer of mirrored spatial structure in visuomotor sequence learning. In M. Knauff, M. Pauen, N. Sebanz, & I. Wachsmuth (Eds.), Proceedings of the 35th Annual Conference of the Cognitive Science Society (pp. 3504-3509). Austin, TX: Cognitive Science Society. ISBN: 978-0-9768318-9-1.
- Chen, N., Tanaka, K., Matsuyoshi, D., & Watanabe, K. (2013) Correlated preference for color and shape, The Proceedings of International Conference on Biometrics and Kansei Engineering, 297-300. ISBN978-0-7695-5019-0.
- Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. (2012) Effects of explicit knowledge on transfer of visuomotor sequence learning. In N. Miyake, D. Peebles, & R. P. Cooper (Eds.), Proceedings of the 34th Annual Conference of the Cognitive Science Society, 1036-1041. Austin, TX: Cognitive Science Society. ISBN 978-0-9768318-8-4.
- Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. (2012) Effects of feedback on an energy conservation task under uncertainty. Proceedings of the International Conference on Kansei Engineering and Emotion Research, KEER2012, 616-621. ISBN:978-986-03-2488-4.
- Chien, S., Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. (2012) Effects of exposure to and simulated purchase of green products on altruistic and pro-environmental behaviors. Proceedings of the International Conference on Kansei Engineering and Emotion Research, KEER2012, 610-615. ISBN:978-986-03-2488-4.
- Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. (2011) Overestimation and underestimation in learning and transfer. The Proceedings of International Conference on Biometrics and Kansei Engineering, 81-86, J. Guerrero, California:IEEE Computer Society. ISBN:978-0-7695-4512-7.
- Tanaka, K., & Yamaoka, T. (2008) Extracting the Components of Elderly People's Capacity in Electrical appliances and Grasping Relationship with the Components. Computer-Human Interaction, Volume 5068, Springer Berlin / Heidelberg, 420-426. ISBN: 978-3540705840.
- Tanaka, K., Tsuji, T., Emoto, Y., & Yamaoka, T. (2007) Comparing the selling points of products with problems of products. IASDR07 PROCEEDINGS Emerging Trends in Design Research, CR-ROM (15 pages).
Oral Presentations in International Conferencess
- Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. (2017/2/1-4) Impacts of cue reliability and explicit instruction on visual attention. 9th International Conference on Knowledge and Smart Technology (KST), Pattaya, Thailand.
- Tanaka, K., Chien, S., Yamamoto, K., & Watanabe, K. (2016/2/3-6) Memory distortion of depth of a visual stimulus for perception and action. 8th International Conference on Knowledge and Smart Technology (KST), Chiangmai, Thailand.
- Ueda, N., Tanaka, K., &Watanabe, K. (2016/2/3-6) Gender differences in visuomotor sequence learning. 8th International Conference on Knowledge and Smart Technology (KST) , Chiangmai, Thailand.
- Yamamoto, K., Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. (2015/1/28-31) The role of global configuration in detection of mirror and translational symmetries. 7th International Conference on Knowledge and Smart Technology (KST) , The Tide Resort Hotel, Thailand.
- Chen, N., Tanaka, K., Namatame, M, & Watanabe, K. (2015/1/28-31) Consistency of color-shape associations in deaf people. 7th International Conference on Knowledge and Smart Technology (KST) , The Tide Resort Hotel, Thailand.
- Chen, N., Tanaka, K., Nagamori, Y., Namatame, M., & Watanabe, K. (2014/9/4-7) Color-grapheme associations in deaf people. The 2nd Conference of Asia Color Association (ACA2014), Taipei, Taiwan.
- Chen, N., Tanaka, K., Mastumoshi, D., Nagamori, Y., Namatame, M., & Watanabe, K. (2014/1/30-31) Color-shape association in deaf and hearing people. Special session on "Recent Advances in Cognitive Science", 6th International Conference on Knowledge and Smart Technology (KST-2014), Burapha University, Thailand.
- Chen, N., Tanaka, K., Matsuyoshi, D., & Watanabe, K. (2013/12/11-14) Cross preference for color combination and shape. The 1st Asia Color Association Conference (ACA2013), Thanyaburi, Thailand.
- Chen, N., Tanaka, K., Matsuyoshi, D., & Watanabe, K. (2013/8/26-30) Associations between colors and shapes in Japanese observers. 5th international congress of international association of societies of design research.(IASDR2013), Tokyo, Japan.
- Chen, N., Tanaka, K., Matsuyoshi, D., & Watanabe, K. (2013/7/5-7) Correlated preference for color and shape. 2013 International Conference on Biometrics and Kansei Engineering (ICBAKE2013), Akihabara, Japan.
- Hosoda, C., Tanaka, K., Tatekawa, M., Honda, M., Osu, R., & Hanakawa, T. (2013/6/20-23) Neural substrate of making it through the goal. Neuro 2013, Kyoto International Conference Center, Japan.
- Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. (2012/8/1-4) Effects of explicit knowledge on transfer of visuomotor sequence learning. COGSCI 2012 - 34th Annual Cognitive Science Conference, Sapporo, Japan.
- Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. (2012/5/22-25) Effects of feedback on an energy conservation task under uncertainty. International Conference on Kansei Engineering and Emotion Research, Penghu, Taiwan.
- Chien, S., Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. (2012/5/22-25) Effects of exposure to and simulated purchase of green products on altruistic and pro-environmental behaviors. International Conference on Kansei Engineering and Emotion Research, Penghu, Taiwan.
- Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. (2011/9/19-22) Overestimation and underestimation in learning and transfer. 2011 International Conference on Biometrics and Kansei Engineering (ICBAKE2011), Takamatsu City, Kagawa, Japan.
- Tanaka, K., & Yamaoka, T. (2008, 7) Extracting the Components of Elderly People's Capacity in Electrical appliances and Grasping Relationship with the Components. Computer Human Interaction 8th Asia-Pacific Conference (APCHI2008), Seoul, Korea.
- Tanaka, K., Tsuji, T., Emoto, Y., & Yamaoka, T. (2007, 11) Comparing the selling points of products with problems of product. IASDR07, Kowloon, Hong Kong.
Poster Presentations in International Conferencess
- Tanaka, T., Watanabe, K., & Tanaka, K. (2020/7/29-8/1) Immediate action-effects facilitate response speed via stimulus-response association, 42nd Annual Virtual Meeting of the Cognitive Science Society, Virtual Meeting
- Loria, T., Tanaka, K., Watanabe, K., & Tremblay, L. (2019/10/19-23) What can audiovisual illusions teach us about gaze vs. action related spatial attention?, Society for Neuroscience, Chicago, USA.
- Ueda, N., Tanaka, K., Maruo, K., Sumiyoshi, T., Watanabe, K. & Hanakawa, T. (2019/8/21-24) Increased central bias in time reproduction in schizophrenia with predominantly positive symptoms. WPA World Congress of Psychiatry, Lisbon, Portugal.
- Oishi, H., Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. (2019/6/25-28) Sense of agency in continuous action is influenced by outcome feedback in one-back trials. The 23rd Meeting of the Association for the Scientific Study of Consciousness, Ontario, Canada
- Loria, T., Hajj, J., Tanaka, K., Watanabe, K., & Tremblay, L. (2019/5/17-22) The deployment of spatial attention during goal-directed action alters audio-visual integration, The 19th annual meeting of the Vision Sciences Society (VSS2019), Florida, USA.
- Tanaka, K. & Watanabe, K. (2019/3/7-9) Sense of agency for action-effect grouping with illusory visual events. International Convention of Psychological Science (ICPS2019) , Paris, France.
- Loria, T., Tanaka, K., Watanabe, K., & Tremblay, L. (2018/11/3-7) Modulation of audio-visual processes at attended vs. unattended spatial locations. Society for Neuroscience, San Diego, USA.
- Loria, T., Hajj, J., Tanaka, K., Watanabe, K., & Tremblay, L. (2018/10/21) Visual attention influences audiovisual event perception and the susceptibility to the fusion illusion. Canadian Society for Psychomotor Learning and Sport Psychology (Proceedings of the SCAPPS 2018 Annual Conference), Toronto, Canada.
- Oishi, H., Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. (2018/6/26-29) Unpredictable feedback of results in continuous action retrospectively influences sense of agency. The 22nd Meeting of the Association for the Scientific Study of Consciousness, Krakow, Poland.
- Loria, T., Tanaka, K., Tremblay, L., & Watanabe, K. (2018/6/14-17) Attentional modulation of multisensory event perception in a voluntary reaching movement. The 19th Annual International Multisensory Research Forum, Toronto, Canada.
- Lasrado, S., Sokhn, N,. Tanaka, K., Watanabe, K., & Caldara, R. (2018/5/18-23) Race at First Sight. The 18th annual meeting of the Vision Sciences Society (VSS2018), Florida, USA.
- Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. (2016/07/24-29) Time evaluation while performing sequential actions. The 31st International Congress of Psychology (ICP2016), Yokohama, Japan.
- Watanabe, K., & Tanaka, K. (2016/7/12-13) Emotional inhibition increases risky decisions in a gambling task. The first meeting of the Society for the Advancement of Judgment and Decision Making Studies, Palma de Mallorca, Spain.
- Tanaka, K., Kawai, T., & Watanabe, K. (2016/7/14-17) Effects of adding a color stimulus sequence to a spatial response sequence on visuomotor sequence learning. The 12th Asia Pacific Conference on Vision, Esplanade Hotel, Fremantle, Australia.
- Lee, R. K., Tanaka, K., Kakizaki, M., & Watanabe, K. (2016/5/13-18) Changes in audiovisual cue utilization strategy when cues become unreliable. Vision Science Society 16th Annual Meeting, Tradewinds Island Resorts, Florida, USA.
- Lee, R. K., Tanaka, K., Hachisuka, K., Okuno, E., & Watanabe, K. (2015/5/13-18) Cleaving to cues that are no longer informative: Audio-visual asymmetry in cue utilization. Vision Science Society 15th Annual Meeting, Tradewinds Island Resorts, Florida, USA.
- Tanaka, K., Chen, N., & Watanabe, K. (2014/7/19-22) The level of categorical knowledge affects visual search efficiency. The 10th Asia-Pacific Conference on Vision (APCV 2014), Takamatsu, Japan.
- Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. (2014/3/12-13) Implicit transfer in visuomotor sequence learning. Conference on Systems Neuroscience and Rehabilitation, Tokorozawa, Saitama, Japan.
- Hosoda, C., Tanaka, K., Tatekawa, M., Honda, M., Osu, R., & Hanakawa, T. (2013/11/8-13) Neural substrate of making it through the goal. Society for Neuroscience, San Diego, USA.
- Tanaka, K., & Watanabe, K. (2013/7/31-8/3) Implicit transfer of mirrored spatial structure in visuomotor sequence learning. The Annual Meeting of the Cognitive Science Society, Berlin, Germany.
- Hosoda, C., Tanaka, K., Osu, R., Honda, M., & Hanakawa, T. (2012/10/13-17) The more/less ability, the more/less brain structure. Society for Neuroscience, New Orleans, USA.
- Tanaka, K., Ono, F., & Watanabe, K. (2012/7/2-6) The relationship of two numerical magnitudes influences spatial shifts of attention. Association for the Scientific Study of Consciousness, University of Sussex, Brighton, UK.
国内会議 (2019~)
- 田中拓海・島根大輔・渡邊克巳・田中観自(2020/9/8-9/10)行動の直後に知覚された刺激の記憶は増強される 日本心理学会第84回大会 東洋大学白山キャンパス(ウェブ開催)
- 大石博之・田中観自・渡邊克巳 (2019/11/29-12/1)行為選択の自由度が行為―結果間の時間知覚に与える影響. 日本基礎心理学会第38回大会, 神戸大学(兵庫県神戸市)(ポスター発表)
- 杉本 海里・田中観自・渡邊克巳 (2019/11/29-12/1)自己生成された接近-回避に関する命題が図形の評価に与える影響.日本基礎心理学会第38回大会, 神戸大学(兵庫県神戸市)(ポスター発表)
- 田中拓海・渡邊克巳・田中観自 (2019/11/29-12/1)課題非関連なフィードバックによる反応の促進は運動に依存する.日本基礎心理学会第38回大会, 神戸大学(兵庫県神戸市)(ポスター発表)
- 大石博之・田中観自・渡邊克巳 (2019/5/26)継続行為における行為主体感の予期的・遡及的変調.日本認知心理学会第17回大会,京都テルサ(京都府京都市)(ポスター発表)

Call for participation
当研究室では,心理学実験に参加していただける大学生・大学院生を募集しています.
Contents of experiment
主な実験内容は,画面に呈示される視覚刺激に反応したり,聞こえてくる聴覚刺激に反応したりするもので,TVゲームのような簡単なものです.心理実験といっても,あなたのこころがわかったり,性格が判断されることはありません.データは統計的に処理され,許可なく個人情報を公表することはありません.各実験の詳細は,配信される案内に書かれていますので,そちらをご参照ください.
Registration
当研究室では,九州大学に所属する大学生・大学院生のみを対象に実験参加者の募集をしています.実験の案内を受け取るためには,LINEにて友人登録していただく必要があります.LINEによる登録を希望される方は,以下のメールアドレスに学籍番号とお名前を連絡してください.確認後に,招待用の資料を送付いたします.
tanaka.lab.experiment(at)gmail.com
Time
実験時間:実験内容によって異なりますが,基本的には60分か90分の拘束になります.通常,九州大学の時間割に沿って開始・終了します.1限目であれば8時40分から開始し,10時10分には終了するという流れになります.授業間での空きコマ等自由な時間があるときに参加をご検討ください.90分の拘束時間の中で,同意書の説明,実験参加,休憩,謝礼手続きなどが含まれており,90分連続で実験を行い続ける訳ではありません.詳細は案内メールに書かれていますので,都度ご検討してください.
Place
九州大学伊都キャンパスのセンター3号館で行われることが多いです.しかし,実験内容によっては,オンラインやイーストゾーンの実験棟など別の建物で行う場合もあります.詳細は案内メールを確認してください.
Reward
実験参加の謝礼は,全国のコンビニエンスストア等で使用可能なQUO card となります.拘束時間や実験の内容によって変動しますが,目安としては,1時間につき1,000円のクオカードの配布となります.
Important reminder
実験参加の予約をしたにもかかわらず無断欠席した方,連絡なく大幅な遅刻をした方,また実験中の参加態度が芳しくない方(居眠りなど)などは,今後の参加をご遠慮いただきます.予めご了承ください.
Online Experiment
現在,当研究室では,オンライン実験も並行して行っています.オンライン実験では,指定された時間にMicrosoft Teamsにアクセスし,実験者から実験の説明を受けていただきます.実験参加の同意後,指定されたリンクにアクセスし,自分自身のPCで実験を受けていただくという流れになっています.その他の詳細については,実験案内に書かれていますので,参加希望の方はLINEの友人申請を行ってください.

jobs/Admissions
Jobs
Current status: no available
現在,研究員,RA,秘書の雇用に関する募集は行っておりません.
日本学術振興会が提供する特別研究員PDの受入研究室として当研究室を検討される場合,田中観自(kanji.tanaka(at)artsci.kyushu-u.ac.jp)まで,お気軽にご連絡ください.その後の面談等を通じて,実際に当研究室で希望する研究計画が遂行できるかどうかを判断していただき,最終的に受入研究室として希望するかどうかを決めていただければと思います.
Admission
田中観自研究室は,2021年10月より九州大学大学院人間環境学府行動システム専攻心理学コースに所属しています(田中の本所属は基幹教育院であり,人間環境学府を兼担する形となります).本研究室では主に,ヒトの認知処理過程に関する実験心理学的研究(例えば,自己主体感,系列学習,反応促進・抑制,感覚間協応,クロスモーダル)とその教育を行っています.教員の取り組んでいる主なテーマは,”Research”セクションをご確認ください.
現在,学内外からの研究生,修士課程,および博士後期課程進学希望者を募集しています.本研究室の指導方針等についての詳細はこちらのページをご確認ください.入学試験に関する詳細情報は人間環境学府のウェブサイトでご確認下さい.
進学を希望する学生の見学やオンライン面談をいつでも歓迎しています(入試を受けられる前に必ず一度はコンタクトしてください).ウェブページに記載されていない様々な情報を得ることもできると思います.研究室見学や教員との面談を希望される場合,田中観自(kanji.tanaka(at)artsci.kyushu-u.ac.jp)まで,お気軽にご連絡ください.将来,大学教育・研究を含め心理学的知識を活かせる幅広い分野で活躍することを目指す,意欲あふれる自律した人を募集します.

links/Alumni
Instituion
- Kyushu University, Faculty of Arts and Science
- Kyushu University, Graduate School of Human-Environment Studies
Collaborators
- Prof. Katusmi Watanabe, Waseda University
- Prof. Haider Hilde, University of Cologne
- Prof. Roberto Caldara, University of Fribourg
- Dr. Sarah Esser, University of Cologne
- Dr. Tessei Kobayashi, NTT
- Dr. Yuko Okumura, NTT
- Dr. Kentaro Yamamoto, Kyushu University
- Dr. Takumi Tanaka, The University of Tokyo
- Dr. Kyoshiro Sasaki, Kansai University
- Dr. Loria Toristan, Tronto University
- Dr. Natsuki Ueda, National Institute of Mental Health, National Center of Neurology and Psychiatry
- Dr. Maiko Kobayashi, Waseda University
- Dr. Ryoji Onagawa, Waseda University
- M.Sc. Felice Tavera, University of Cologne
- Assistant, Mr. Toshiyuki Numata, Waseda University(2016-2017), The University of Tokyo(2018-2019)
Alumni
- Takumi Tanaka (2020/Apr - 2021/Mar)
- Rena Iimori (2021/Jan - 2024/Mar)
- Kumiko Fujinaga (2021/Jan - 2024/Mar)
Post doc
Technical Assistant